GPS 좌표를 화면 좌표로 변환하기
by Jeongjin Kim
GPS 좌푯값으로 지도의 어느 위치인지 표시하기 위한 좌표 변환 과정을 남기고자 한다. 클라우드 지도 서비스를 이용해야 할 만큼 정밀한 지도가 필요하지 않고, 상대적으로 좁은 지역 정보를 화면상에 표시해야 할 때 유용할 것이라 생각한다. 또한 위치정보표기 요청이 수초 단위로 짧아서 클라우드 서비스를 활용하기에는 비용이 많이 발생할 것이라고 판단이 될 때 또한 대안이 될 것이다.
아래 사진은 인천 송도에 있는 공원 지도를 캡처한 사진이다. 공원에서 관리하는 자산, 예를 들어 관리용 카트 같은것에 GPS 수신기가 있어 실시간 위치 모니터링이 필요하다고 해보자.
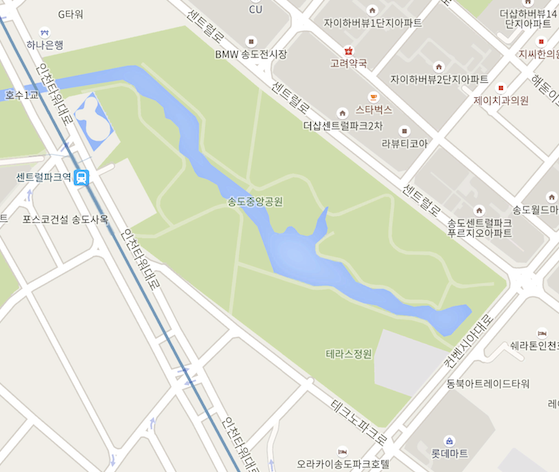
공원이 정북 방향으로 되어 있지 않고 비스듬하게 있는데 이 상태로는 모니터링 시스템에 바로 넣기에는 공간이 아깝다. 이 사진을 화면에 꽉 차도록 회전시켜보자. 그런데 구글 지도나 네이버 지도 등 화면을 돌리는 기능이 없다. 모바일 앱에는 양 손가락으로 돌리면 돌아가는데 PC용은 지원하지 않는다. 사실, 이 돌리기 기능만 있어도 돈이 조금 들더라도 클라우드 서비스에서 제공하는 API를 썼을 것 같다.
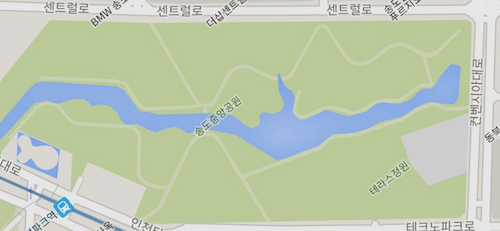
이렇게 회전된 상태에서 GPS 값 위도, 경도를 입력받았을 때 지도의 어느 위치인지 표시할 수 있도록 Screen X, Y 값을 계산하고 그리는 것이 이 포스트의 최종 목표이다.
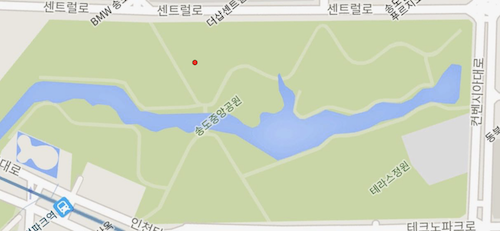
GPS 값을 표기하는 방법 다양한데 문제를 단순화하기 위해서 구글 맵에서 GPS값을 표시하는 방법인 도분초를 십진수로 표기하는 방법을 사용한다.
실제 지도를 회전해서 화면 좌표계로 변환하는 작업은 각 모서리를 서로 맞추고 크기 또한 비율대로 축소 확대하는 과정이다.
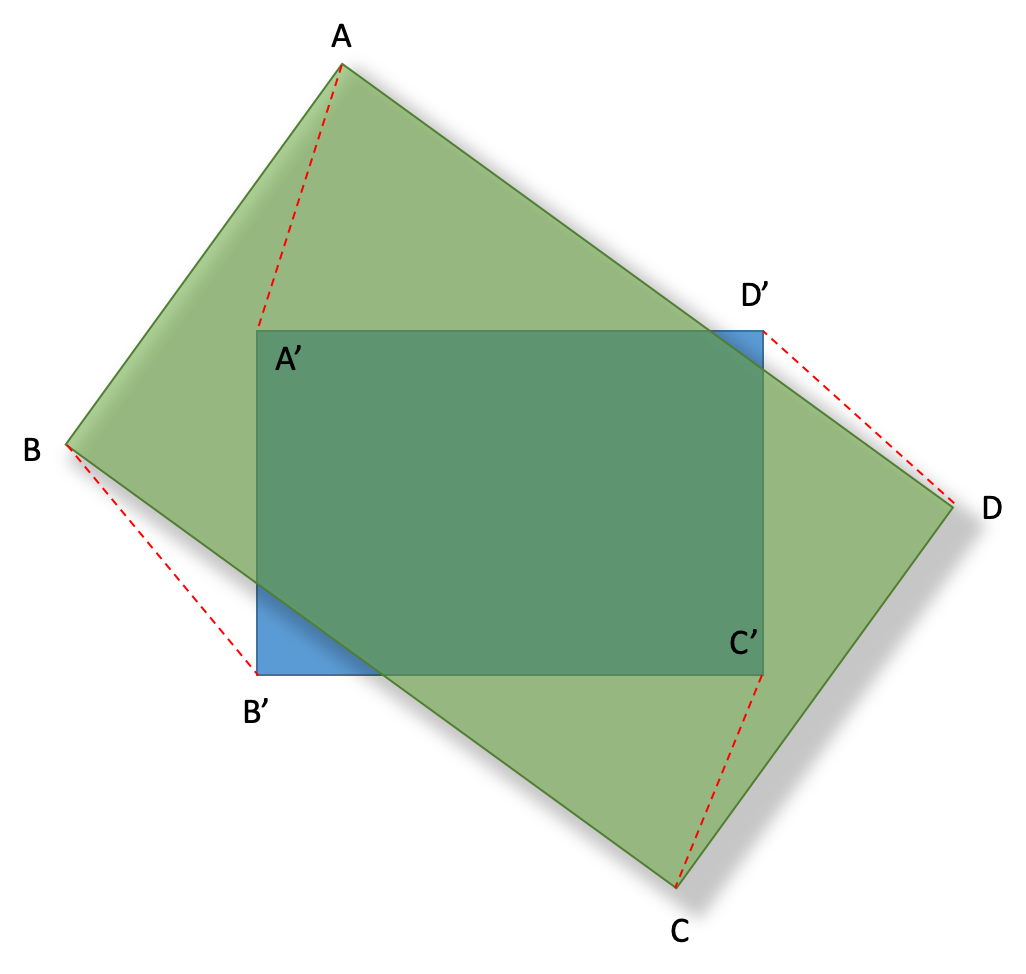
다시 말하면 특정 꼭지점을 기준으로 화면 좌표계와 지도를 수평이 되도록 Θ만큼 회전한 다음 비율을 조절하는 것이다.
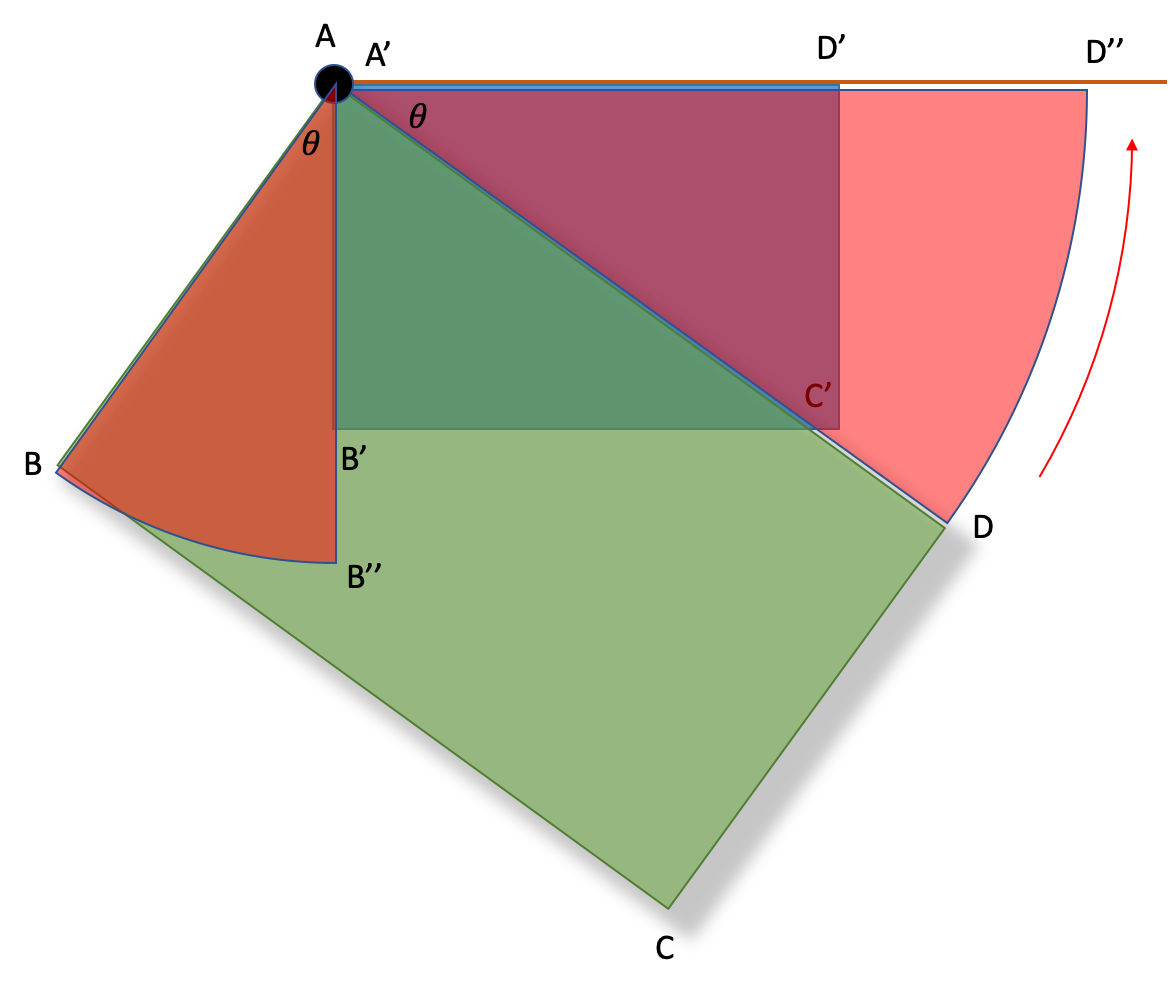
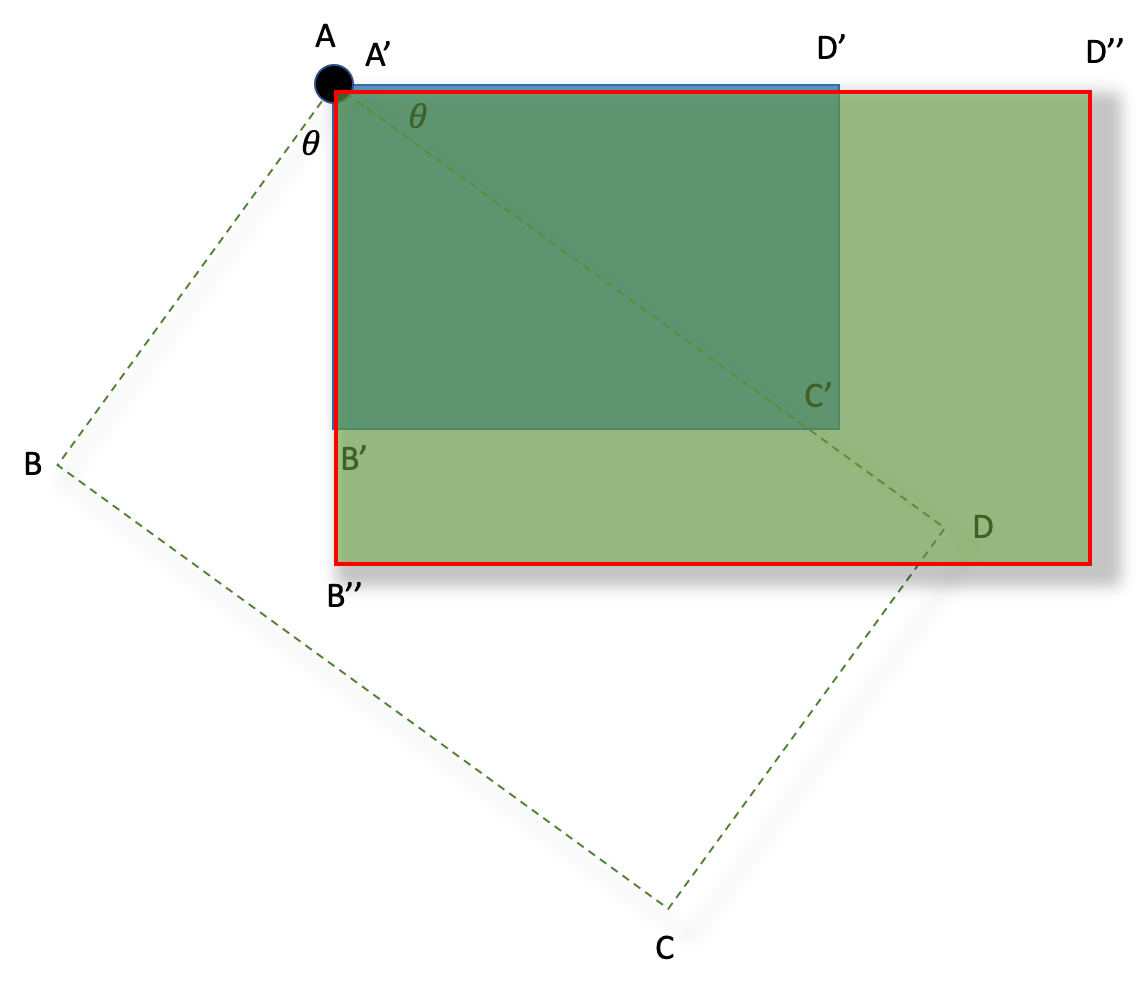
데이터 준비
지도 이미지를 표시할 영역을 DIV tag로 지정하고 백그라운드 이미지로 위에서 회전시킨 이미지를 넣는다.
백그라운드 DIV tag에 onclick 이벤트 핸들러를 넣어주고 밑에 find 라는 링크를 넣어서 찾고자 하는 GPS 값의 위치를 계산하도록 할 것이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<style>
.back {
width: 1024px;
height: 480px;
background-color: powderblue;
background-image: url(songdo.jpg);
background-size: contain;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body style="margin: 0px; padding:0px">
<div id="main" class="back" onclick="mapOnclickHandler()">
<canvas id="myCanvas" style="width:100%; height:100%"></canvas>
</div>
<div id="result">
</div>
<a href="#" onclick="find()">find</a>
</body>
</html>
DIV tag의 oneclick 이벤트 핸들러 mapOnclickHandler() 함수는 화면에 클릭한 위치의 화면 좌표와 그 지점의 GPS 값을 입력을 받을 수 있도록 한다. 데이터는 Array 타입의 전역변수를 선언해서 사용한다.
let data = new Array();
function mapOnclickHandler() {
var cX = event.clientX;
var cY = event.clientY;
var gps = prompt("GPS");
var lat = Number(gps.split(",")[0]);
var lon = Number(gps.split(",")[1]);
data.push({ x: cX, y: cY, lat: lat, lon: lon })
}
구글 지도에서 기준점이 될만한 위치를 클릭해서 그 지점의 GPS값을 복사한다. 여기서는 37.394692, 126.638895 이다.
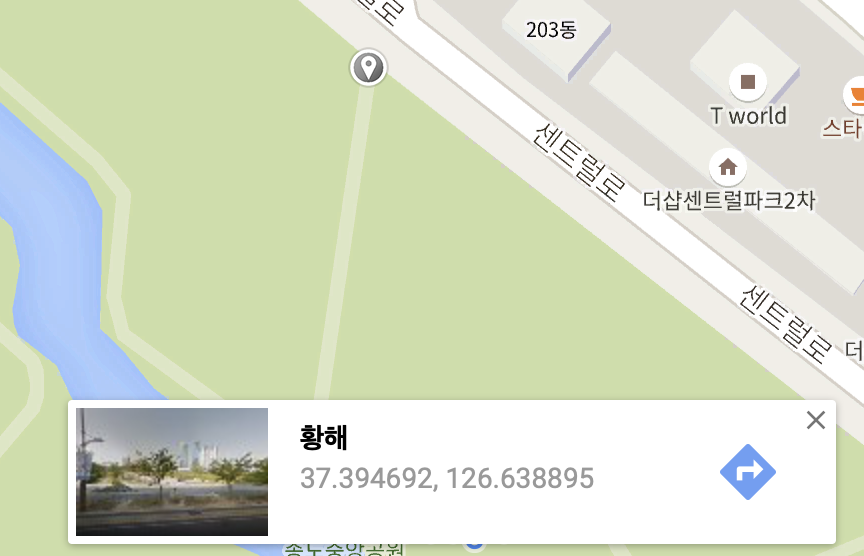
이 값을 개발하고 있는 화면에서 구글 지도에서 클릭한 곳과 같은 위치를 클릭해 GPS값을 입력한다.
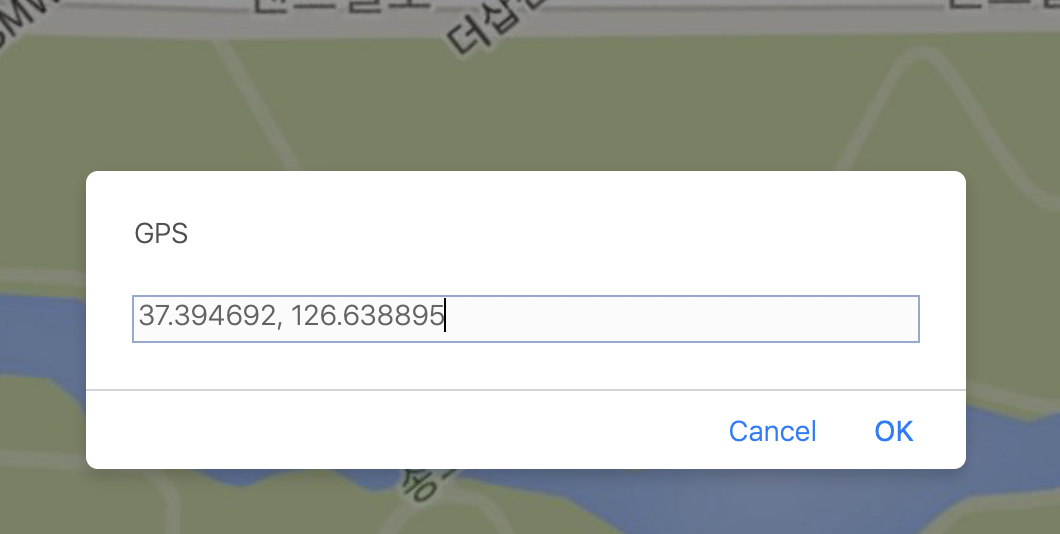
지금 입력한 지점이 회전축이 된다. 이 회전축을 기준으로 수평이 되게 할 위치 한 곳과 그림에서 B’’ 정도 될만한 위치 한 곳을 클릭하여 GPS 정보를 입력한다.
지도에서는 교차로 부근과 공원내 보도 교차지점 정보를 입력했다.
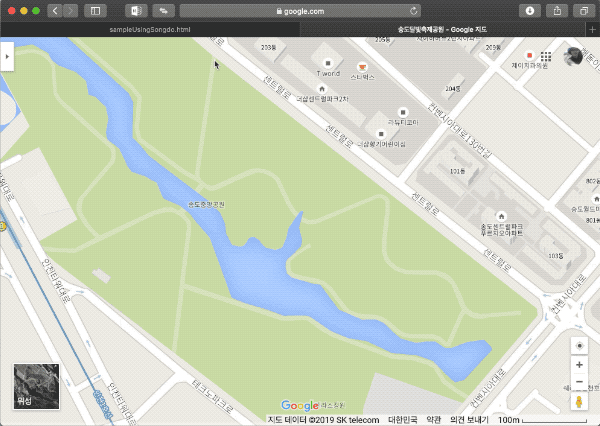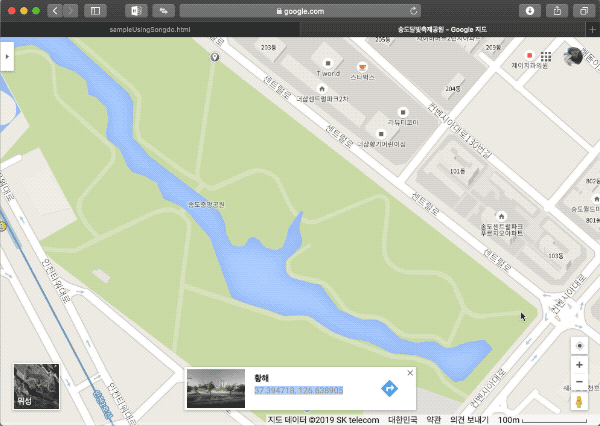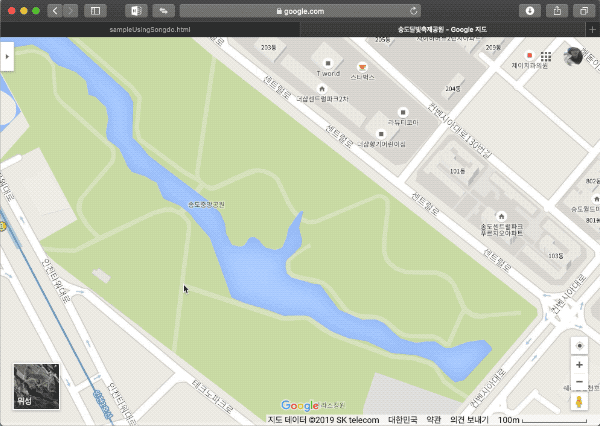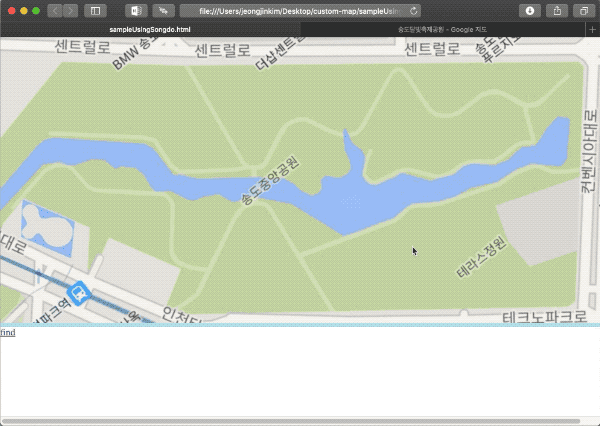
이렇게 온라인 지도에서 가져온 GPS값과 실제 표시될 지도의 스크린 위 좌표를 매핑하는 것으로 계산을 하기 위한 데이터 준비가 완료됐다.
회전 각도 구하기
가장 먼저 구해야할 값은 온라인 지도를 지정한 원점을 기준으로 얼마만큼 회전했을 때 이미지 지도처럼 수평이되는지 각도를 계산하는 것이다.
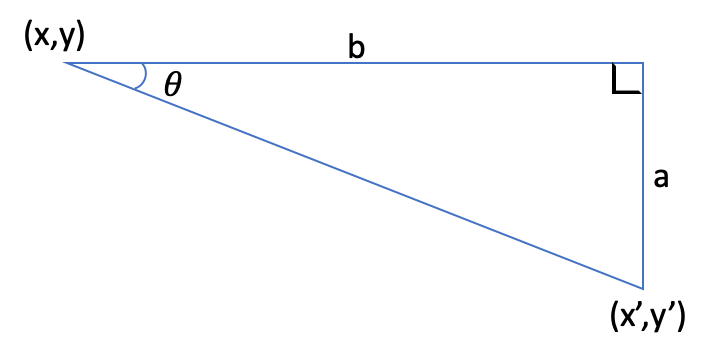
위 도형에서
\[\tan\theta=\frac{a}{b}\]𝜃 로 정리하면
\[\theta = arctan\frac{a}{b}\]이 수식으로 처음 입력한 3점중 첫 번째, 두 번째 GPS 값으로 각도를 구할 수 있다. 각도를 구하기 위한 함수를 한 정의한다.
/**
* 원점과 y값이 같은 임의의 점을 잇는 선분과, 원점과 지정한 점을 잇는 선분이 이루는 각도
* The angle between the line connecting the origin and any point with the same y value and the line connecting the origin and the specified point.
* @param {number} origin_x
* @param {number} origin_y
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @param {boolean} is_rad 리턴받을 각도가 Rad 여부
*/
function calcTheta(origin_x, origin_y, x, y, is_rad) {
const a = y - origin_y;
const b = x - origin_x;
const theta = Math.atan(a / b);
if (is_rad) {
return theta;
} else {
return theta * (180 / Math.PI);
}
}
이제 처음 입력한 값들을 이 function에 넣어서 각도를 구해야 하는데 먼저 정의해야 할 상수와 function이 몇 가지 있다.
위에서 정의한 함수 calcTheta가 정확한 값을 반환하게 하려면 파라미터의 값의 단위가 서로 같아야 정확한 값을 구할 수 있다.
x값은 위도이고 y값은 경도이기 때문에 서로 비교할 수 없다. 두 값을 비교하기 위해 한쪽으로 단위를 맞춰야 한다.
단위를 변환하는 function을 정의한다.
/**
* 입력된 경도를 위도로 단위를 변경한다.
* @param {number} lonValue 경도
*/
function convertUnitToLat(lonValue) {
return lonValue * distancePerLon / distancePerLat;
}
/**
* 입력된 위도를 경도로 단위를 변경한다.
* @param {number} LatValue 위도
*/
function convertUnitToLon(LatValue) {
return LatValue * distancePerLat / distancePerLon;
}
위 function에는 distancePerLon 과 distancePerLat 의 정의가 필요하다. 이를 위해 지구 반지름, 인천의 대략적인 위도가 필요하다.
const targetLon = 37.3; //인천의 위도
const radiusOfEarth = 6371.009; //지구 반지름(km)
const circumferenceOfEarth = 2 * Math.PI * radiusOfEarth; //지구 둘레
const distancePerLat = circumferenceOfEarth / 360; //경도당 거리(km)
const distancePerLon = Math.cos(targetLon * Math.PI / 180) * circumferenceOfEarth / 360; //위도당 거리(km)
회전 각도를 계산한다.
let theta = calcTheta(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(data[1].lon), data[1].lat, true) * -1;
계산된 회전값은 약 0.667\(\mathit{rad}\) 즉 약 37.6\(\,^{\circ}\)로 계산됐다.
좌표 회전하기
두 번쨰, 세 번째 입력한 좌표를 앞서 계산한 각도만큼 회전했을 때 좌표를 계산한다. 회전변환행렬은 위키를 참조하기 바란다. 회전변환행렬은 아래와 같이 정리되는데 이 수식을 이용한다.
\[x' = x cos\theta - y sin\theta\] \[y' = x sin\theta + y cos\theta\]/**
* 원점에서 떨어진 임의의 점을 지정한 각도만큼 회전했을 때 좌표
* Coordinates when rotated by the specified angle
* @param {number} origin_x
* @param {number} origin_y
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @param {number} theta
* @param {boolean} is_rad 입력한 각도가 Rad 여부
*/
function calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(origin_x, origin_y, x, y, theta, is_rad) {
const rebased_x = x - origin_x;
const rebased_y = y - origin_y;
let rad_theta;
if (is_rad) {
rad_theta = theta;
} else {
rad_theta = theta * (Math.PI / 180);
}
const rotatedX = (rebased_x * Math.cos(rad_theta)) - (rebased_y * Math.sin(rad_theta));
const rotatedY = (rebased_x * Math.sin(rad_theta)) + (rebased_y * Math.cos(rad_theta));
const xx = rotatedX + origin_x;
const yy = rotatedY + origin_y;
return { x: xx, y: yy };
}
회전 변환 function을 이용해서 두 좌표를 회전한 위치값을 저장한다.
// 회전후 좌표 계산
// 두 번째 입력한 위치 회전변환
let tempCoordi = calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(data[1].lon), data[1].lat, theta, true);
tempCoordi.x = convertUnitToLon(tempCoordi.x);
data[1].lon_rotated = tempCoordi.x;
data[1].lat_rotated = tempCoordi.y;
// 세 번째 입력한 위치 회전변환
let tempCoordi2 = calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(data[2].lon), data[2].lat, theta, true);
tempCoordi2.x = convertUnitToLon(tempCoordi2.x);
data[2].lon_rotated = tempCoordi2.x;
data[2].lat_rotated = tempCoordi2.y;
GPS값을 화면 좌표계로 변환 방정식 만들기
화면 좌표계의 값과 GPS 값의 관계를 방정식으로 정의하기 위한 function을 만든다.
/**
* 평면위에 점 (origin_x,origin_y) 와 (to_x, to_y) 를 지나는 직선의 기울기와 절편을 계산하여 방정식을 만든다.
* The slope and intercept of the line passing through the point (origin_x, origin_y) and (to_x, to_y)
* @param {number} origin_x
* @param {number} origin_y
* @param {number} to_x
* @param {number} to_y
*/
function makeLinearEquation(origin_x, origin_y, to_x, to_y) {
const x_variation = to_x - origin_x;
const y_variation = to_y - origin_y;
const slope = y_variation / x_variation;
const intercept = origin_y - (slope * origin_x);
return {slope: slope, intercept: intercept};
}
위도와 경도에 대해서 각각 방정식을 만든다.
let lonQuation;
let latQuation;
// 위도, 경도 방정식 만들기
lonQuation = makeLinearEquation(data[0].lon, data[0].x, data[1].lon_rotated, data[1].x);
latQuation = makeLinearEquation(data[0].lat, data[0].y, data[2].lat_rotated, data[2].y);
GPS 좌표를 스크린 좌표로 변환
화면 좌표를 계산하기 위한 모든 준비는 완료됐다. 이제 위도, 경도 값을 입력으로 화면에서 좌표가 무엇인지 계산만 하면 된다. 이를 위한 function을 정의한다.
/**
* 화면상 좌표를 계산한다.
* @param {number} lat 위도
* @param {number} lon 경도
*/
function calcScreenCoordinates(lat, lon) {
let tempCoordi = calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(lon), lat, theta, true);
tempCoordi.x = convertUnitToLon(tempCoordi.x);
let x = lonQuation.slope * tempCoordi.x + lonQuation.intercept;
let y = latQuation.slope * tempCoordi.y + latQuation.intercept;
return { x: x, y: y };
}
계산된 위치 그리기
x, y좌표를 입력받아서 작은 원을 그리는 function을 정의한다.
function drawCircle(x, y) {
let context = setupCanvas(document.getElementById('myCanvas'));
let centerX = x;
let centerY = y;
let radius = 5;
context.beginPath();
context.arc(centerX, centerY, radius, 0, 2 * Math.PI, false);
context.fillStyle = 'red';
context.fill();
context.lineWidth = 1;
context.strokeStyle = '#003300';
context.stroke();
}
function setupCanvas(canvas) {
// Get the device pixel ratio, falling back to 1.
var dpr = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
// Get the size of the canvas in CSS pixels.
var rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
// Give the canvas pixel dimensions of their CSS
// size * the device pixel ratio.
canvas.width = rect.width * dpr;
canvas.height = rect.height * dpr;
var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Scale all drawing operations by the dpr, so you
// don't have to worry about the difference.
ctx.scale(dpr, dpr);
return ctx;
}
테스트
구글 지도에서 찾고자 하는 위치의 GPS값을 가져와서 개발한 화면에서 찾아보면 정확하게 위치를 표시하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
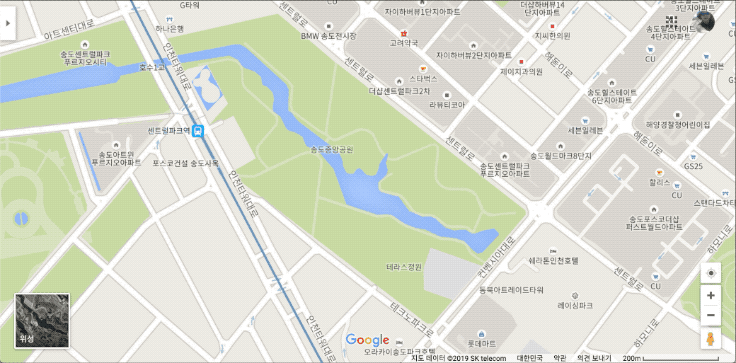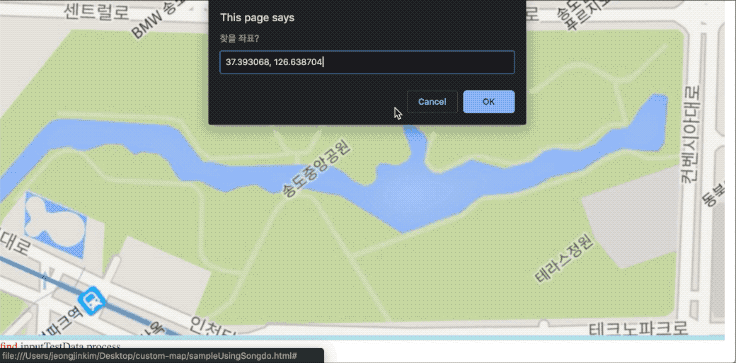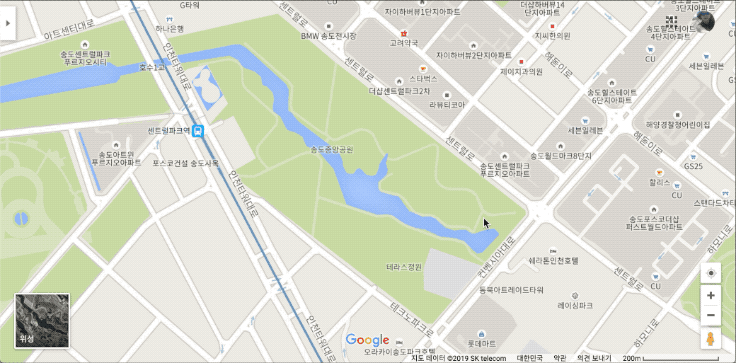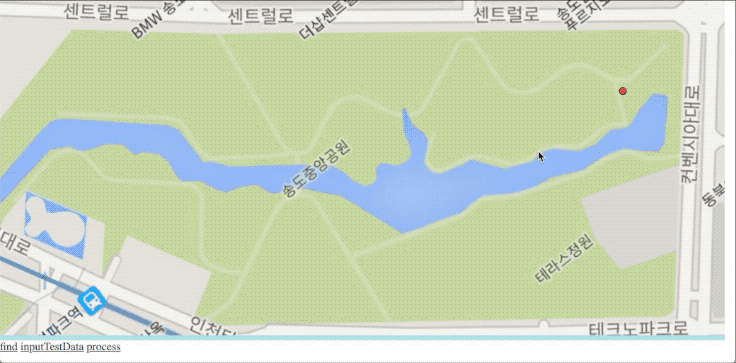
소스
UI
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="commonSongdo.js"></script>
<style>
.back {
width: 1024px;
height: 480px;
background-color: powderblue;
background-image: url(songdo.jpg);
background-size: contain;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
<script>
let data = new Array();
let theta;
let lonQuation;
let latQuation;
const targetLon = 37.3; //인천의 위도
const radiusOfEarth = 6371.009; //지구 반지름(km)
const circumferenceOfEarth = 2 * Math.PI * radiusOfEarth; //지구 둘레
const distancePerLat = circumferenceOfEarth / 360; //경도당 거리(km)
const distancePerLon = Math.cos(targetLon * Math.PI / 180) * circumferenceOfEarth / 360; //위도당 거리(km)
function process(){
if (data.length < 3) return;
// 각도 계산
theta = calcTheta(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(data[1].lon), data[1].lat, true) * -1;
// 회전후 좌표 계산
// 두 번째 입력한 위치 회전변환
let tempCoordi = calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(data[1].lon), data[1].lat, theta, true);
tempCoordi.x = convertUnitToLon(tempCoordi.x);
data[1].lon_rotated = tempCoordi.x;
data[1].lat_rotated = tempCoordi.y;
// 세 번째 입력한 위치 회전변환
let tempCoordi2 = calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(data[2].lon), data[2].lat, theta, true);
tempCoordi2.x = convertUnitToLon(tempCoordi2.x);
data[2].lon_rotated = tempCoordi2.x;
data[2].lat_rotated = tempCoordi2.y;
// 위도, 경도 방정식 만들기
lonQuation = makeLinearEquation(data[0].lon, data[0].x, data[1].lon_rotated, data[1].x);
latQuation = makeLinearEquation(data[0].lat, data[0].y, data[2].lat_rotated, data[2].y);
}
function inputTestData() {
data.push({x: 307, y: 46, lat: 37.394709, lon: 126.638884});
data.push({x: 956, y: 42, lat: 37.391163, lon: 126.644613});
data.push({x: 503, y: 367, lat: 37.391419, lon: 126.638358});
}
</script>
</head>
<body style="margin: 0px; padding:0px">
<div id="main" class="back" onclick="mapOnclickHandler()">
<canvas id="myCanvas" style="width:100%; height:100%"></canvas>
</div>
<div id="result">
</div>
<a href="#" onclick="find()">find</a>
<a href="#" onclick="inputTestData()">inputTestData</a>
<a href="#" onclick="process()">process</a>
</body>
</html>
Lib
commonSondo.js
/**
* 지도에서 클릭된 스크린 위치와 입력한 GPS값을 저장한다.
*/
function mapOnclickHandler() {
let cX = event.clientX;
let cY = event.clientY;
let gps = prompt("GPS");
let lat = Number(gps.split(",")[0]);
let lon = Number(gps.split(",")[1]);
data.push({ x: cX, y: cY, lat: lat, lon: lon })
}
/**
* GPS 좌표를 입력받아 화면좌표를 구하고 그린다.
*/
function find() {
var gps = prompt("찾을 좌표?");
var lat = Number(gps.split(",")[0]);
var lon = Number(gps.split(",")[1]);
var xy = calcScreenCoordinates(lat, lon);
console.info(xy);
drawCircle(xy['x'], xy['y']);
}
/**
* 입력된 경도를 위도로 단위를 변경한다.
* @param {number} lonValue 경도
*/
function convertUnitToLat(lonValue) {
return lonValue * distancePerLon / distancePerLat;
}
/**
* 입력된 위도를 경도로 단위를 변경한다.
* @param {number} LatValue 위도
*/
function convertUnitToLon(LatValue) {
return LatValue * distancePerLat / distancePerLon;
}
/**
* 원점과 y값이 같은 임의의 점을 잇는 선분과, 원점과 지정한 점을 잇는 선분이 이루는 각도
* The angle between the line connecting the origin and any point with the same y value and the line connecting the origin and the specified point.
* @param {number} origin_x
* @param {number} origin_y
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @param {boolean} is_rad 리턴받을 각도가 Rad 여부
*/
function calcTheta(origin_x, origin_y, x, y, is_rad) {
const a = y - origin_y;
const b = x - origin_x;
const theta = Math.atan(a / b);
if (is_rad) {
return theta;
} else {
return theta * (180 / Math.PI);
}
}
/**
* 원점에서 떨어진 임의의 점을 지정한 각도만큼 회전했을 때 좌표
* Coordinates when rotated by the specified angle
* @param {number} origin_x
* @param {number} origin_y
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @param {number} theta
* @param {boolean} is_rad 입력한 각도가 Rad 여부
*/
function calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(origin_x, origin_y, x, y, theta, is_rad) {
const rebased_x = x - origin_x;
const rebased_y = y - origin_y;
let rad_theta;
if (is_rad) {
rad_theta = theta;
} else {
rad_theta = theta * (Math.PI / 180);
}
const rotatedX = (rebased_x * Math.cos(rad_theta)) - (rebased_y * Math.sin(rad_theta));
const rotatedY = (rebased_x * Math.sin(rad_theta)) + (rebased_y * Math.cos(rad_theta));
const xx = rotatedX + origin_x;
const yy = rotatedY + origin_y;
return { x: xx, y: yy };
}
/**
* 평면위에 점 (origin_x,origin_y) 와 (to_x, to_y) 를 지나는 직선의 기울기와 절편을 계산하여 방정식을 만든다.
* The slope and intercept of the line passing through the point (origin_x, origin_y) and (to_x, to_y)
* @param {number} origin_x
* @param {number} origin_y
* @param {number} to_x
* @param {number} to_y
*/
function makeLinearEquation(origin_x, origin_y, to_x, to_y) {
const x_variation = to_x - origin_x;
const y_variation = to_y - origin_y;
const slope = y_variation / x_variation;
const intercept = origin_y - (slope * origin_x);
return {slope: slope, intercept: intercept};
}
/**
* 화면상 좌표를 계산한다.
* @param {number} lat 위도
* @param {number} lon 경도
*/
function calcScreenCoordinates(lat, lon) {
let tempCoordi = calcCoordinatesAfterRotation(convertUnitToLat(data[0].lon), data[0].lat, convertUnitToLat(lon), lat, theta, true);
tempCoordi.x = convertUnitToLon(tempCoordi.x);
let x = lonQuation.slope * tempCoordi.x + lonQuation.intercept;
let y = latQuation.slope * tempCoordi.y + latQuation.intercept;
return { x: x, y: y };
}
function drawCircle(x, y) {
let context = setupCanvas(document.getElementById('myCanvas'));
let centerX = x;
let centerY = y;
let radius = 5;
context.beginPath();
context.arc(centerX, centerY, radius, 0, 2 * Math.PI, false);
context.fillStyle = 'red';
context.fill();
context.lineWidth = 1;
context.strokeStyle = '#003300';
context.stroke();
}
function setupCanvas(canvas) {
// Get the device pixel ratio, falling back to 1.
var dpr = window.devicePixelRatio || 1;
// Get the size of the canvas in CSS pixels.
var rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
// Give the canvas pixel dimensions of their CSS
// size * the device pixel ratio.
canvas.width = rect.width * dpr;
canvas.height = rect.height * dpr;
var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Scale all drawing operations by the dpr, so you
// don't have to worry about the difference.
ctx.scale(dpr, dpr);
return ctx;
}
Subscribe via RSS
